Remote work offers flexibility and access to a broader talent pool, but it also creates new entry points for cybercriminals. When your team works from home, coffee shops, or anywhere with Wi-Fi, every laptop becomes a new front door to your company's network.
Home networks, personal devices, and public Wi-Fi don’t have the same level of security as the office. You also have employees using unauthorized AI tools and outdated VPNs that can’t handle the traffic. For small and mid-sized business owners, all of this can feel overwhelming.
In this article, we walk you through the common remote work security risks and provide practical ways to keep your distributed workforce safe without slowing them down.
Why Remote Work Security Belongs in Your IT Strategy
Top Cyber Threats for Remote Workers
Cybersecurity Basics for Your Remote Team
Why Remote Work Security Belongs in Your IT Strategy
Back in the day, most company data lived safely behind the walls of a secure office network. IT teams focused on protecting that perimeter with firewalls and other tools. Now, that perimeter is gone. Employees log in from all over, using all kinds of devices, and cybercriminals have taken note.
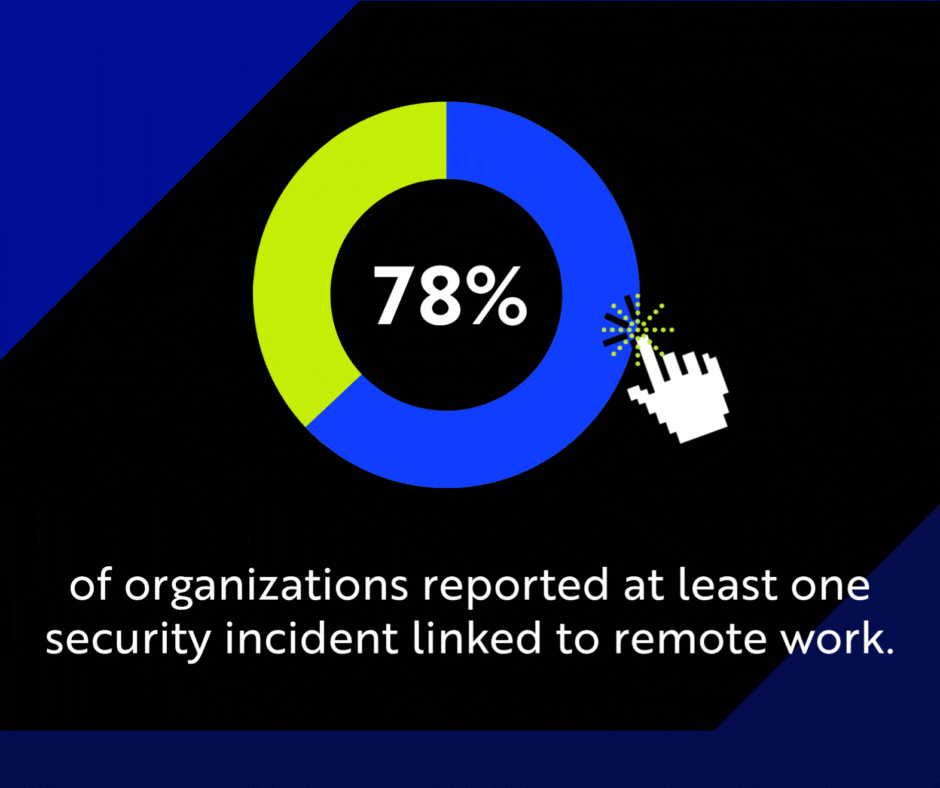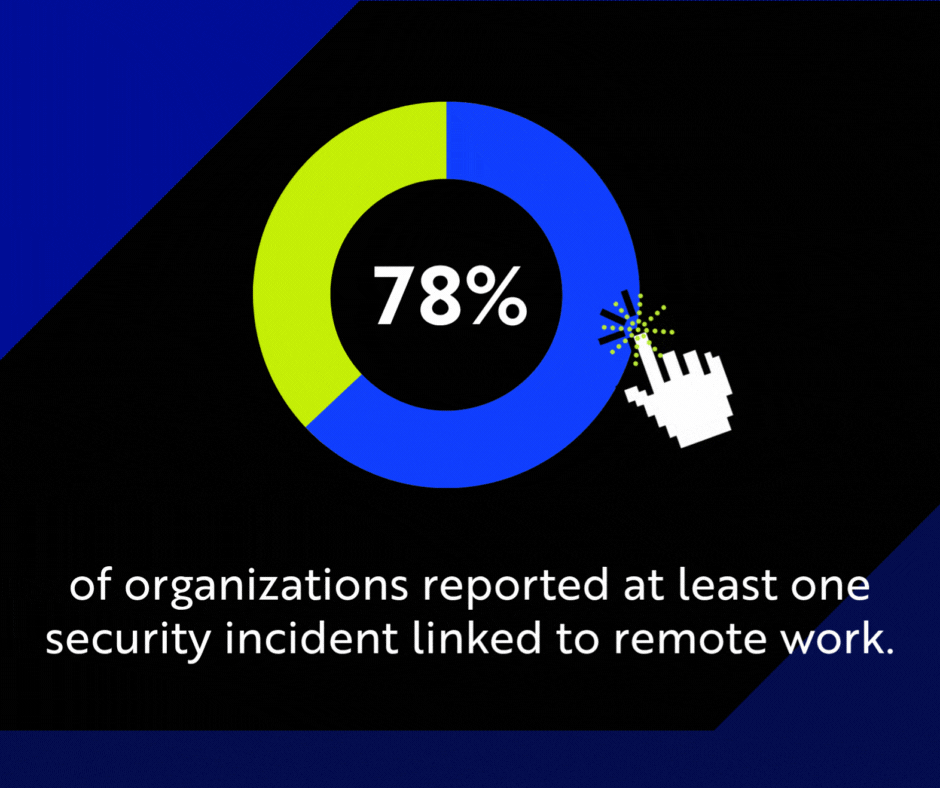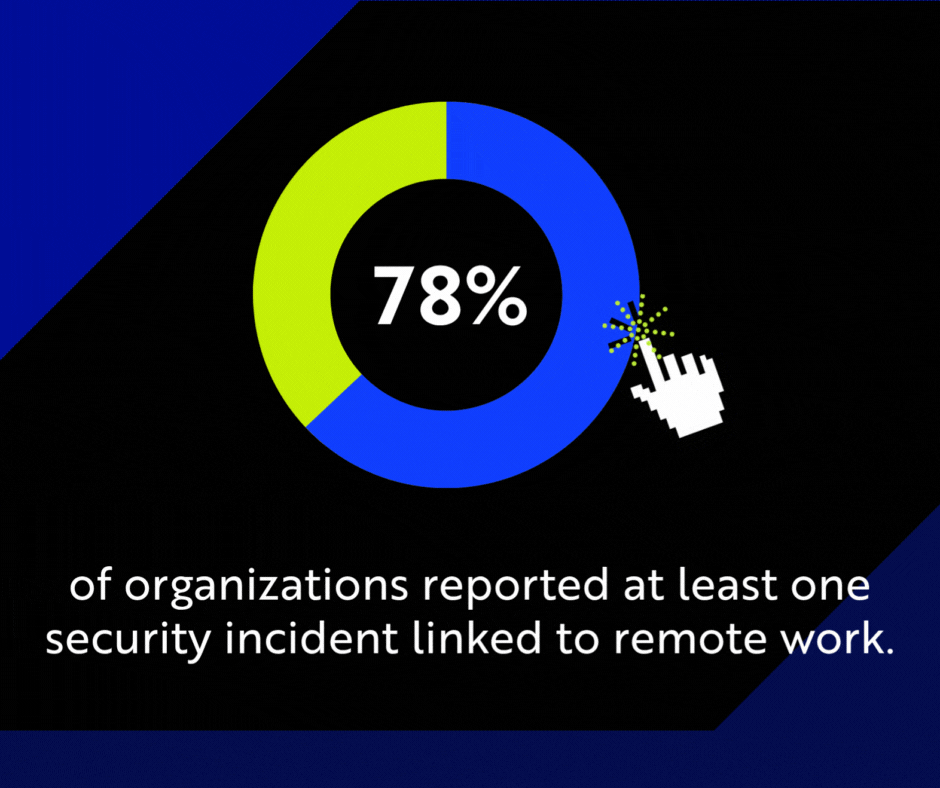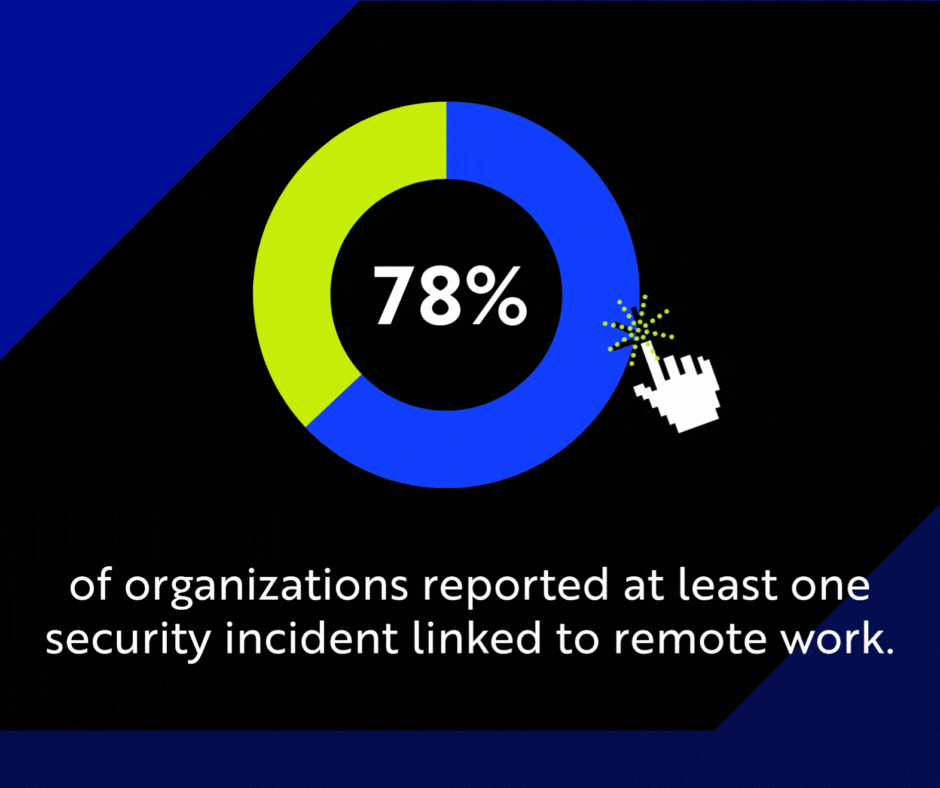
In fact, studies show that 78% of organizations reported at least one security incident linked to remote work. Many small businesses don’t have the same level of visibility or response tools as large enterprises, which makes them prime targets for cyber attacks.
To make things worse, 73% of these small business owners say their employees don’t take cybersecurity seriously. Many organizations weren’t set up for this kind of distributed work model, and the resources to manage it can feel out of reach.
Top Cyber Threats for Remote Workers
When your team isn’t in the office, it brings unique security challenges. Here’s what to watch out for:
Phishing Scams
Phishing is still the number one way hackers gain access to your systems. Cybercriminals craft convincing emails that appear to be from IT support or even senior executives, tricking employees into sharing their login credentials or downloading malicious attachments. Without the ability to check with a coworker in person, it’s easier to fall for these scams.
Weak or Reused Passwords
Raise your hand if you’re guilty of using the same password for work, banking, and personal accounts. It’s tempting because it makes life easier, but this habit puts both your personal life and business at risk when all your employees do the same.
Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks
Office Wi-Fi is usually locked down with strong security, but home networks? Not so much. Many home routers still use default passwords and outdated security settings. Public Wi-Fi is even worse. These networks are often not encrypted, making it easy for hackers to steal your sensitive data.
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD)
The line between work and personal devices is blurry. Many employees use their own laptops or mobile devices for work. These devices, referred to as "Bring Your Own Device" (BYOD), may lack essential security software like antivirus and firewalls. They might also have unpatched software vulnerabilities or family members may use them, increasing the risk of cyber attacks.
Shadow AI
Your employees aren’t waiting for AI policies. They’re already using AI tools to boost productivity. Remote work settings make it even easier for this experimentation to happen without oversight. Unfortunately, many of these tools lack proper encryption or data protection, which means sensitive data could be exposed or stored on third-party servers without your knowledge.
According to research from IBM, 20% of companies have experienced a data leakage because of employees using GenAI. Plus, if employees use AI tools to generate or process sensitive data, it could lead to compliance issues.
Legacy VPNs
Legacy VPNs weren’t built for today’s remote work demands. Many of them can’t scale, run slowly, or are just misconfigured, leaving security gaps. When performance lags, employees may bypass the VPN entirely, putting company data at risk and opening the door to cyber threats.
Cybersecurity Basics for Your Remote Team
You don’t need to overhaul your entire operation to improve security. These best practices can make a big difference in safeguarding your teams from cyber threats:
1. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA
Passwords alone aren’t enough anymore. Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, like a code sent to your phone or a fingerprint scan. This small step can block up to 99% of automated attacks, according to Microsoft. Even if a hacker gets a password, multi-factor authentication can stop them in their tracks.
2. Secure Home Networks and Mobile Devices
Help your team lock down their home Wi-Fi by changing default router passwords, enabling WPA2 or WPA3 encryption, and keeping firmware updated. For company-owned devices, an endpoint security solution can help monitor for cyber threats and enforce security policies automatically.
If employees use personal devices for work, establish clear guidelines. Require them to:
- Keep their systems updated
- Use antivirus software
- Enable device encryption and lock screens
3. Provide Regular Employee Training
Technology can’t do it all. Your people are your first line of defense. Hold short, practical training sessions on:
- How to spot phishing scams
- Why strong passwords matter
- How to handle suspicious messages or security incidents
Make it interactive and engaging. The goal of employee training is to ingrain cybersecurity into your company culture, not to lecture.
4. Encrypt Everything
Encryption scrambles your data so it’s useless to hackers. Make sure all company devices have full-disk encryption and that data is encrypted both when it’s sent and when it’s stored.
5. Establish Zero Trust Network Access
Unlike traditional VPNs, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) grants users access only to the specific resources they are authorized to use, versus the entire network. This approach is scalable, faster, and ensures employees only access what they need, protecting sensitive data while improving remote work for all.
6. Keep Collaboration Tools Secure
Apps like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Slack make remote work possible, but they can also expose data if permissions aren’t set correctly. Review sharing settings, remove old accounts, and monitor third-party app connections regularly.
7. Implement Endpoint Protection and Monitoring
Managed detection and response (MDR) tools help you see what’s happening across every connected device. They can automatically isolate suspicious activity before it spreads. If you don’t have an in-house IT team, consider partnering with a managed service provider (MSP) that offers this as part of their cybersecurity services. It’s affordable, and it saves you from dealing with alerts 24/7.
New Era, New Rules
Cybercriminals love a small to mid-sized business. They are more likely to pay a ransom quickly and probably don’t have a dedicated IT department to watch out for trouble. As a small business owner, you’re likely more focused on growing your company than worrying about protecting your remote workforce. At CompassMSP, we’re here to help you keep it that way.
Join our upcoming webinar, where you will learn about remote work security risks and how to protect your remote workforce. CompassMSP Senior vCISO, Richard Mendoza, and Watchguard’s Senior Product Manager, Stephen Helm, break down the security challenges of remote work and share practical cybersecurity tips to padlock your front door.







